

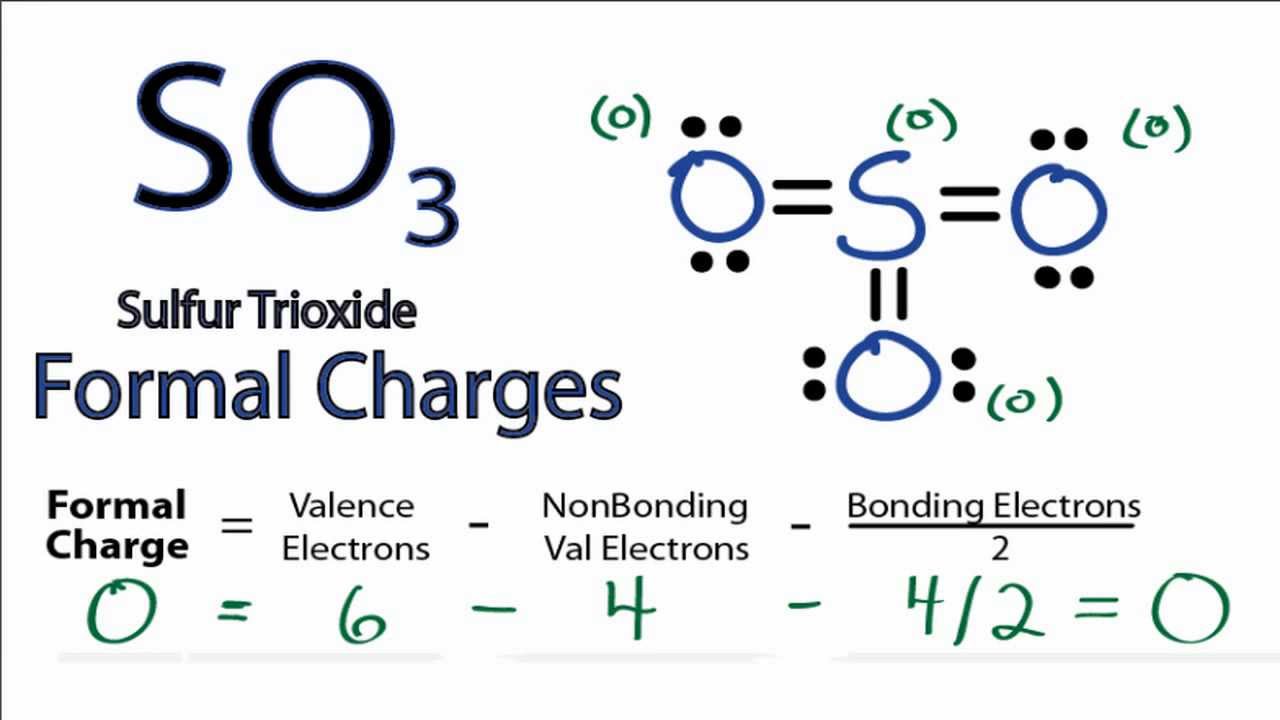
Synthesis Ī convenient synthesis involves flash pyrolysis of certain oximes. The structure of the molecule has been determined by microwave spectroscopy with the following bond-lengths - C-H: 1.027(1) Å, C-N: 1.161(15) Å, N-O: 1.207(15) Å. Determine the formal charge for carbon in the following structures. Determine the formal charge for the nitrogen and oxygen atoms (both values and signs are required) H H 5. We use the following equation to calculate formal charge on an atom in Lewis structure. Formal charge on each atom is due to difference in valence electrons in an isolated atom and number of electrons assigned to that atom in a Lewis structure. formal charges to all the atoms in the following Lewis structure of hydrazoic. (Both values and signs should be provided) - H-6-H H-O: H-Cö-H H.C0-CHE CHE 4. Each atom in a Lewis structure for a molecule or ion will have formal charge. Which of the following skeletal structures are most likely for them. The chemical that actually has that structure, isofulminic acid (a tautomer of the actual fulminic acid structure) was eventually detected in 1988. In the following structures, indicate the formal charge on oxygen atoms. It wasn't until the 1966 isolation and analysis of a pure sample of fulminic acid that this structural idea was conclusively disproven. The formal charge is the charge on the atom in the molecule. Identifying formal charges helps you keep track of the electrons. This is often useful for understanding or predicting reactivity. Calculating some Formal Charges Calculate the formal charge on oxygen in the hydronium ion shown: Oxygen is in Group VI and has 6 valence electrons in the ground state. In order to calculate the formal charges for ClO4- we'll use the equation:Formal charge of valence electrons - nonbonding val electrons - bonding el. Structure įulminic acid was long believed to have a structure of H–O–N +≡C −. An atom can have the following charges: positive, negative, or neutral, depending on the electron distribution. This chemical was known since the early 1800s through its salts and via the products of reactions in which it was proposed to exist, but the acid itself was not detected until 1966. For historical reasons, the fulminate functional group is understood to be −O−N +≡C − as in isofulminic acid whereas the group −C≡N +O − is called nitrile oxide. įulminate is the anion or any of its salts. It is an isomer of isocyanic acid ( H−N=C=O) and of its elusive tautomer, cyanic acid ( H−O−C≡N), and also of isofulminic acid ( H−O−N +≡C −).

We hope that you find a good answer and gain the knowledge about this topic of science.Fulminic acid is an acid with the formula HCNO, more specifically H−C≡N +−O −. EXERCISE Formal Charge What is the formal charge on the nitrogen atom in this molecule O-1 0 O +1 O +2 Recheck Next (3 of 7) 1st attempt Incorrect Formal charge is calculated by the following formula: Formal charge group number - lone pair electrons - 1/2 bond pair electrons Try the calculation again. This is the resonance form C with a formal charge on every atom:įor $math_tag_14, the resonance form B is the preferred structureĪbove is the solution for “ Add formal charges to each resonance form of HCNO below., Please add formal charges for each…“. This is the Lewis structure for A resonance form: You can create a new resonance form by changing the electron pairs and bonds around an atom in a resonance format. A Lewis structure that has no formal charge on an atom is a favorable structure.Ī resonance form is any Lewis structure that exists for a molecule, ion or other substance. Non-bonding electrons can be placed on atoms in pairs.Ī molecule may have multiple Lewis structures. A triple bond is made using six electrons. Four electrons are required to form a double bond. Using Equation 2.3.1, the formal charge on the nitrogen atom is therefore Formal Charge of N (5 valence e-) - (0 lone pair e-) - (1/2 x 8 bond pair e. Of electrons shared in bonds/2 In structure A. Two electrons are required to form a single bond. Formula to calculate formal charge, Formal charge valence electrons - no. The number of valence electrons within an atom is equal to its group number in a periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
